Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the landscape of smart buildings, optimizing energy efficiency, improving security, and automating building management.
In fact, the AI in Smart Buildings and Infrastructure market, valued at $13.4 billion in 2024, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21.58%, highlighting its increasing adoption and impact. Similarly, the smart building market is expected to grow 22% by 2029, demonstrating the rapid shift toward AI-driven infrastructure.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in smart buildings will expand beyond automation into predictive and generative applications, allowing structures to respond intelligently to their environments. To put this into perspective, this blog will explore 10 key AI use cases in smart buildings and highlight 5 real-world examples demonstrating its impact.

What Are “AI Buildings”?
While the term “AI Buildings” is not yet widely recognized in the AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) industry, it is gaining traction due to the increasing integration of AI in smart buildings and digital twin technology.
An “AI Building” or “artificial intelligence building” refers to a structure that integrates artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and improve occupant experiences. These buildings use smart automation, data analytics, and machine learning to manage systems including lighting, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), security, and energy consumption.
For example, The Edge in Amsterdam, Netherlands is known as one of the smartest buildings in the world as it uses AI for energy efficiency and space optimization. The Edge exemplifies how a dynamic and collaborative work environment can seamlessly align with the highest standards of sustainability.
Recognized as the world’s most sustainable office building, it holds the highest rating ever recorded by the Building Research Establishment (BRE), the global authority on sustainable buildings.
The project earned a BREEAM ‘Outstanding’ certification for new construction, achieving an impressive score of 98.36% by integrating cutting-edge smart technologies with a holistic approach to sustainability.
What Is a Smart Building?
A smart building is a structure that employs advanced technologies to enhance operational efficiency, comfort, and safety for its occupants. Integrating systems such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security, and energy management, allows smart buildings to optimize performance through automation and real-time data analytics.
“The value of smart building deployments is projected to grow by 95% to $14bn by 2026 globally. This growth, up from $7bn in 2024, will be driven by sustainability initiatives and the need for cost reductions in building management.” —Report from Juniper Research.
A Brief History of Smart Buildings
Here’s a brief history of events that occurred and led to the creation of the term “smart building”:
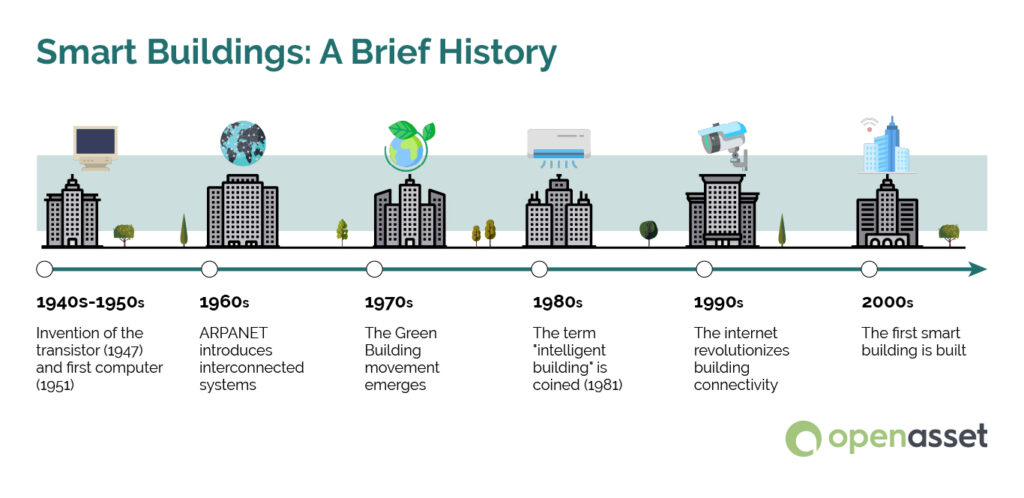
- 1940s-1950s: The invention of the transistor in 1947 and the first computer in 1951 laid the groundwork for digital control systems in buildings.
- 1960s: The development of ARPANET, a precursor to the internet, introduced the concept of interconnected systems.
- 1970s: Environmental concerns and energy crises led to the Green Building movement, emphasizing energy efficiency.
- 1980s: The term “intelligent building” was coined in 1981, focusing on automated control of HVAC systems to improve efficiency.
- 1990s: The public availability of the internet in 1991 revolutionized building connectivity, enabling remote monitoring and control.
- 2000s: With the introduction of the internet, the term “Smart Building” was coined and the first smart building was built.
- 2010s-Present: Advancements in artificial intelligence and data analytics have further optimized building operations, leading to the development of highly responsive and efficient smart buildings.
Smart Building Features
Smart buildings incorporate a variety of advanced features to enhance efficiency, comfort, and security. Key features of intelligent buildings include:
- Interconnected Systems: Integration of various building systems—such as HVAC, lighting, alarms, and security—into a single IT-managed network infrastructure.
- Energy Efficiency: Utilization of smart processes to automate and control building systems le heating, lighting ventilation, and air conditioning, leading to reduced energy consumption.
- Eco-Friendliness: Implementation of sustainable practices and technologies to minimize environmental impact.
- Remote Operation: Ability to monitor and control building systems rotely, enhancing convenience and responsiveness.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Continuous gathering and analysis of data from building systems to inform maintenance, optimize performance, and improve occupant comfort.
- Advanced Security Measures: Incorporation of biometric access control, surveillance systems, and fire detection systems to enhance safety.
- Predictive Maintenance: Real-time monitoring of equipment health and performance to detect potential issues early, reducing downtime and repair costs.
- Occupant Comfort: Personalized environmental settings, such as temperature and lighting preferences, to improve the user experience.
Technologies Used in Smart Buildings
Smart buildings create responsive environments that meet the evolving needs of occupants while promoting sustainability and operational efficiency. To do so, smart buildings leverage a range of advanced technologies to enhance efficiency, comfort, and safety.
Key technologies used in smart buildings include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, such as smart sensors and actuators, collect and exchange data to monitor and control building systems like lighting, HVAC, and security.
- Building Automation Systems (BAS): BAS provides centralized control of a building’s various systems, enabling automated adjustment to optimize performance and energy efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML analyze data from building systems to predict maintenance needs, optimize energy consumption, and improve occupant comfort.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM involves creating digital representations of a building’s physical and functional characteristics, facilitating better planning, design, and management throughout its lifecycle.
- Energy Management System (EMS): An EMS monitors and controls energy usage, integrating renewable energy sources and storage solutions to enhance sustainability.
- Smart Lighting Systems: These systems use sensors and controls to adjust lighting based on occupancy and natural light availability, reducing energy consumption.
- Advanced Security Systems: Integrating access control, surveillance cameras, and intrusion detection, these systems enhance building security and occupant safety.
- Climate-Adaptive Building Shells: These dynamic structures adjust their properties in response to environmental conditions, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
What Are the Benefits of Using AI in Smart Buildings?
AI-powered smart buildings offer a range of environmental, economic, and operational benefits, making them more sustainable, cost-effective, and efficient. Here are the benefits in more detail:
- Environmental Benefits
- Energy Efficiency: AI optimizes HVAC, lighting, and energy consumption, reducing waste and carbon footprint.
- Sustainable Operations: AI integrates with renewable energy sources, improving resource management.
- Economic Benefits
- Cost Savings: Predictive maintenance reduces repair costs, and AI-driven energy management lowers utility expenses.
- Higher Property Value: Smart buildings with AI-driven systems attract tenants and investors, increasing market appeal.
- Operational Efficiencies
- Automation and Optimization: AI enhances building automation systems (BAS) for real-time control of lighting, security, and climate.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI identifies potential system failures before they occur, preventing costly downtime.
- Improved Security and Safety: AI-powered surveillance, access control, and anomaly detection enhance building security.
“Different smart building technologies are in different places, but we’re absolutely at the early stages of deploying smart building technology and understanding what additional benefits it has.” —Joe Aamidor of Aamidor Consulting
How AI Is Impacting Architecture, Engineering, and Construction
AI is significantly transforming the AEC industry by enhancing design processes, automating tasks, and improving project management. Here’s how AI is transforming the AEC industry:
Design Optimization
AI-powered generative design tools enable architects and engineers to rapidly explore a multitude of design possibilities, optimizing layouts for efficiency, sustainability, and aesthetics. These tools assist in creating designs that are not only innovative but also aligned with specific project requirements.
Complete Routine Tasks With Automation
By automating repetitive tasks, AI allows professionals to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of projects. For example, AI can handle data analysis, scheduling, and resource allocation, thereby streamlining workflows and reducing the potential for human error.
Enhanced Project Management
AI enhances project management by providing predictive analytics that forecast potential delays and budget overruns. This foresight enables proactive decision-making, ensuring projects stay on schedule and within budget.
Improved Safety and Quality Control
In construction, AI-powered systems monitor site conditions in real-time, identifying safety hazards and ensuring compliance with quality standards. This leads to safer work environments and higher-quality outcomes.
How Is AI Used in Smart Buildings? 10 Use Cases
We understand AI and smart buildings, but what about AI in smart buildings? Here are 10 uses cases of how AI is used in smart buildings:
1. Energy Efficiency With AI
Buildings are significant contributors to CO2 emissions, accounting for nearly 40% of global energy-related carbon output.
AI plays a crucial role in reducing energy consumption in smart buildings by learning occupancy patterns, weather conditions, and real-time energy demand. In fact, AI can potentially deliver energy savings of up to 20% in buildings.
Instead of relying on static schedules, AI dynamically adjusts HVAC systems, lighting, and even window shading to maximize efficiency while maintaining comfort.
For example, an AI-driven smart thermostat can lower heating or cooling in unoccupied areas, while advanced energy management systems (EMS) can predict peak energy usage and shift non-essential functions to off-peak hours.
According to a review paper, the use of AI can yield an energy efficiency improvement of 10.2% to 40%, with Model Predictive Control (MPC) being the most effective AI technology for energy.
AI can also integrate with renewable energy sources such as solar panels by forecasting energy production and balancing it with consumption needs.
2. Security and Safety With AI-Powered Protection and Threat Detection
According to recent market research, the “safety and security management” segment within the smart building market holds the largest market share, currently estimated at around 35.2%, highlighting the significant focus on security features in smart building technology.
“It’s [smart technology in a building] required and, if you think of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and you apply it to buildings, having a safe and secure workplace is the most important factor.” —Joe Aamidor, Aamidor Consulting
Smart buildings leverage AI-enhanced surveillance systems, biometric access control, and real-time threat detection to improve security. This can be done through AI-powered cameras, which differentiate between normal activity and suspicious behavior, alerting security personnel before an incident escalates.
For example, facial recognition and license plate scanning can restrict access to authorized personnel while AI-driven anomaly detection can recognize security threats, such as unauthorized entries or unattended objects in sensitive areas.
Advanced cloud-based video analytics, along with AI-driven software, including machine learning and deep learning, can reduce false alarms by 90% or more.
Moreover, AI also enhances fire detection and emergency response, analyzing smoke detector data and triggering alerts faster than traditional systems.
3. Prevent Breakdowns With Predictive Maintenance and Capabilities
Traditional maintenance strategies rely on scheduled checkups or reactive repairs after a breakdown occurs. However, AI-driven predictive maintenance revolutionizes this by continuously monitoring equipment performance, identifying early warning signs of failure, and recommending proactive repairs before major issues arise.
Unlike traditional methods that schedule inspections quarterly or annually, AI-powered solutions offer continuous monitoring and instant alerts upon detecting anomalies. According to Mose Solar Manufacturing, this proactive approach can cut maintenance costs by 25-30% and increase equipment lifespan by up to 20%.
For example, AI sensors in HVAC systems can detect pressure fluctuations, abnormal vibrations, or temperature inconsistencies, predicting when components might fail. In fact, AI predictive maintenance can reduce breakdowns by up to 70%.
Additionally, AI also assesses data from elevators, electrical grids, and water systems, reducing downtime and cutting costs. In fact, according to recent reports, predictive analytics can reduce unplanned downtime by up to 50% and reduce maintenance costs by 25-30%.
4. Increased Precision and Reduced Errors
AI minimizes human errors in design, engineering, and construction by automating complex calculations, validating structural soundness, and ensuring compliance with safety standards. AI-powered tools improve accuracy in cost estimation, material selection, and regulatory adherence, reducing budget overruns and design flaws.
For example, AI tools like Buildots use computer vision and AI to track real-time construction progress, identifying discrepancies between plans and actual execution.
Moreover, AI-driven clash detection software in BIM (Building Information Modeling) identifies potential structural conflicts before construction starts, avoiding costly rework.
For example, During Heathrow Airport’s expansion, BIM played a crucial role in coordinating architectural, structural, and MEP systems. Clash detection tools identified over 40,000 potential conflicts before construction, preventing costly errors. This proactive approach saved millions in rework costs and helped keep the project on schedule.
5. Smarter Control Over Infrastructure With Smart Building Automation Systems (BAS)
According to recent market reports, the global Building Automation Systems (BAS) market is expected to reach a value of around $150 billion by 2032 with a CAGR of around 7.9%, driven by growing demand for energy efficiency, sustainability initiatives, and integration with IoT technologies in smart buildings.
Building Automation Systems (BAS) are at the heart of AI-driven smart buildings, controlling everything from lighting and HVAC to elevators and security. AI enhances BAS by analyzing building-wide data in real time. This optimizes systems based on usage patterns and environmental conditions.
For example, AI-powered smart HVAC systems adjust airflow and temperature dynamically, while intelligent lighting controls dim or brighten areas based on occupancy and natural daylight levels.
AI can also integrate with IoT-connected devices to streamline communications between different building components, reducing inefficiencies.
6. Resource Optimization
One of AI’s key contributions to resource management is its ability to analyze large data sets quickly and accurately. AI enhances resource management by analyzing space utilization, energy consumption, and operational needs in real time. For example, AI-driven occupancy sensors can help facility managers redesign office layouts based on actual usage, improving efficiency in conference rooms, co-working spaces, and common areas.
Additionally, AI optimizes water usage by detecting leaks in plumbing systems, ensuring more sustainable building management. AI can also enhance waste management by predicting waste generation patterns and optimizing recycling efforts.
7. Enhanced Project Management
By 2030, 80% of project management processes—including task management, scheduling, and reporting— will be fully automated or AI-augmented, extending to complex areas such as risk identification and resource optimization.
AI significantly improves construction project management by providing predictive analytics, automated scheduling, and real-time risk assessment. AI-driven tools analyze historical project data, weather conditions, supply chain fluctuations, and labor availability, allowing firms to adjust schedules dynamically and prevent costly delays.
In fact, AI-driven project management tools are expected to reduce project failures by 30% by 2025.
One example of a project management tool is Procore’s AI-powered construction management platform, which helps project managers streamline workflows, analyze project data, and optimize timelines.
AI can also assist in contractor and supplier coordination, ensuring that resources arrive exactly when needed, and reducing idle labor costs.
Moreover, generative AI will become a critical asset in decision-making, influencing 50% of project management decisions by 2027 by analyzing vast datasets and offering data-driven insights.
8. Digital Twins for Smarter Decision-Making
Buildings integrated with digital twin technology have proven highly energy-efficient, with up to a 20% reduction in energy usage.
A digital twin is an AI-powered virtual replica of a physical building, continuously updated with real-time data from sensors, IoT devices, and historical trends. These digital models allow architects, engineers, and facility managers to simulate different scenarios and optimize building performance before making physical changes.
In fact, some companies report that products starting out as digital twins have 25% fewer quality issues when they enter production.
For example, before making HVAC upgrades, an AI-powered digital twin can simulate airflow and energy consumption, ensuring the best solution is chosen. Digital twins can also model wear and tear on materials, predicting when repairs will be needed.
Additionally, smart buildings augmented with digital twin technologies have shown a potential increase in property value by 7-20%.
9. Enhanced Design Exploration
AI is revolutionizing architectural design by enabling rapid exploration of multiple design options, optimizing for sustainability, cost-efficiency, and structural integrity. In fact, according to recent data, AI design tools can cut costs by up to 70%, speed up design cycles by 50%, and reduce prototyping expenses by 30%.
Generative design tools powered by AI analyze constraints such as material availability, environmental impact, and spatial efficiency to produce functional yet innovative designs.
For example, AI-driven tools like Autodesk’s Generative Design can evaluate thousands of design variations in minutes, helping architects identify the most structurally sound and cost-effective layouts.
AI is also being used in parametric design, where advanced algorithms automatically adjust elements like facade shapes based on solar exposure, improving energy efficiency.
10. Win More Bids With AI
Winning bids in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry requires precision, efficiency, and innovation. AI enhances bid preparation by analyzing historical data, optimizing cost estimates, and generating strategic proposals.
With AI-powered automation, firms can reduce human error, create more competitive pricing structures, and tailor bids to client-specific needs. For example, AI tools can analyze past project data to determine the most competitive yet profitable pricing for a proposal.
In fact, contractors utilizing AI-powered bidding software experience a 20% increase in bid win rates, highlighting the competitive advantage these tools offer. Plus, teams using RFP software submit an average of 46% more responses every year.
Additionally, Digital Asset Management (DAM) platforms with AI-powered features tailored to the AEC industry, like OpenAsset, allow firms to quickly compile high-quality, visually compelling bid materials by automating asset organization and retrieval and providing robust AI features.
The Challenges of Leveraging AI in Smart Buildings
Implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) in smart buildings offers numerous benefits, but it also presents several challenges that need to be addressed for successful integration:
Data Privacy and Security
Smart buildings rely on extensive data collection from occupants and systems, including occupant behavior and preferences. This raises concerns about data privacy and vulnerability to cyber-attacks.
Moreover, smart buildings are vulnerable to cyber threats through IoT devices and communication networks. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and compliance with data protection regulations is essential to safeguard sensitive information.
High Implementation and Maintenance Costs
The initial investment for AI integration can be substantial, including costs for advanced technologies, skilled personnel, and ongoing maintenance. The return on investment (ROI) may take time to become evident, making stakeholders hesitant to invest.
Additionally, the complexity of smart building projects can lead to scope variations, resulting in budget increases and potential delays.
Integration With Existing Systems
Integrating AI into existing building infrastructures can be challenging due to compatibility issues with legacy systems. Many smart buildings operate on older infrastructure that may not be compatible with modern AI solutions.
Ensuring seamless communication between new AI-driven technologies and traditional building management systems is crucial for optimal performance.
User Acceptance and Training
Occupants and facility managers may be resistant to adopting AI technologies due to a lack of understanding or trust. Providing adequate training and demonstrating the tangible benefits of AI can help in gaining user acceptance and ensuring effective utilization.
Moreover, to get the most out of AI technologies, skilled personnel are needed to manage, maintain, and troubleshoot AI-driven solutions.
5 Examples of AI in Smart Buildings
We’ve gone over how AI is used in smart buildings, now, let’s take a look at several notable smart space examples that include AI integration in smart buildings:
1. The Edge – Amsterdam, Netherlands
Often hailed as one of the smartest and greenest buildings globally, The Edge utilizes AI to create a highly efficient and personalized work environment. AI systems manage lighting, climate control, and energy usage by analyzing data from a network of sensors, optimizing energy consumption, and enhancing occupant comfort.
2. 45 Broadway – New York City, USA
At 45 Broadway, the implementation of the BrainBox AI system led to a 15.8% reduction in HVAC energy use, resulting in savings of over $42,000 and a significant decrease in the building’s carbon footprint. The AI optimizes temperature settings by analyzing real-time data on weather and occupancy patterns.
3. Verdigris Technologies – AI-Powered Energy Management
Verdigris Technologies’ AI-driven platform boosts energy efficiency in commercial and industrial buildings. Using smart sensors on electrical panels, it analyzes consumption data to identify inefficiencies, enabling energy savings, optimized performance, and predictive maintenance for cost reduction.
4. Zaha Hadid Architects – London, UK
Zaha Hadid Architects has incorporated generative AI tools into its design process, significantly boosting productivity and efficiency. The firm has reduced rendering times and enhanced design innovation by utilizing platforms like Midjourney and Gendo for text-to-image generation and custom AI models.
5. Living Tomorrow – Innovation Campus in Vilvoorde, Belgium
Living Tomorrow is an innovative campus that showcases various AI applications in building management and daily living. The campus features smart home automation systems, AI-driven energy management, and intelligent security solutions. Living Tomorrow demonstrates how AI can create more efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly building environments, providing a glimpse into the future of smart living spaces.
Will AI Be Able to Build Buildings?
AI significantly enhances the construction process through design optimization, smart building automation, and improved project management.
However, while AI currently cannot fully build a building on its own, it is rapidly evolving to become a crucial tool in the construction process. In fact, The global market for Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Construction was estimated at US$1.8 Billion in 2023 and is projected to reach US$12.1 Billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 31.0% from 2023 to 2030.
AI-powered tools assist architects in generating efficient designs, while autonomous machinery, guided by AI, performs tasks like excavation and grading. Additionally, AI improves project management by providing predictive analytics and real-time monitoring, leading to more efficient project execution.
This could potentially reduce build times and costs while still requiring human oversight and skilled labor for complex tasks like framing or wiring.
What the Future of Building With AI Looks Like
As AI adoption increases, the construction industry is experiencing a shift toward smarter, more automated processes that not only enhance productivity but also support environmental goals. In fact, nearly half of all respondents in the construction and design sectors expect the majority of their projects to be environmentally sustainable by the end of this year. Furthermore, 90% of industry respondents believe a shift towards environmental sustainability is on the rise.
One of the most significant advantages of AI in construction is its potential to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions. A recent study published in Nature Communications assessed the impact of AI in commercial buildings across various U.S. climate zones, highlighting its role in equipment management, occupancy monitoring, and operational efficiency.
The findings suggest that AI-driven solutions could lead to an 8% to 19% reduction in energy use and carbon emissions by 2050. When integrated with broader energy efficiency policies and low-emission power sources, AI’s impact becomes even more pronounced-potentially reducing overall energy consumption by 40% and CO₂ emissions by 90% compared to business-as-usual scenarios.
Beyond sustainability in smart buildings, AI is revolutionizing construction efficiency and safety and AI-driven robotics and automation are accelerating construction timelines while minimizing human error.
These advancements are expected to deliver a 40% boost in productivity, helping construction businesses complete projects faster and with fewer resources. Additionally, AI’s ability to monitor safety risks in real time has the potential to reduce workplace accidents by 20%, making job sites safer and reducing liability costs for contractors.
Looking ahead, AI will continue to evolve, becoming an indispensable tool in resource optimization, construction technology, and project management. As AI-powered systems become more sophisticated, the industry can expect more accurate cost estimations, improved material procurement strategies, and even AI-assisted construction site monitoring.
How will AI be used in construction?
AI is utilized in construction to optimize project planning, resource allocation, and risk management. AI systems can predict potential delays, suggest efficient workflows, and improve decision-making processes by analyzing vast amounts of data.
For example, AI-powered tools assist in comprehending contracts, generating design options, optimizing project workflows, and even predicting project outcomes.
How is AI used in building design?
In building design, AI helps architects by generating multiple design alternatives based on specified criteria, such as cost, energy efficiency, aesthetics, and structural integrity. This generative design approach allows for the exploration of innovative solutions that meet project requirements.
For example, AI can generate design alternatives based on specified criteria, helping contractors optimize designs for cost, energy efficiency, building aesthetics, and structural integrity.
Can AI create construction drawings?
Yes, AI can assist in creating construction drawings by automating the drafting process and ensuring accuracy. AI-powered design software can generate detailed 2D and 3D models, incorporating building specifications and compliance standards, thereby reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
For example, AI-powered tools can assist in comprehending contracts, generating design options, optimizing project workflows, and even predicting project outcomes.
Can AI do construction estimating?
AI excels in construction estimating by analyzing historical data, current market trends, and project specifics to provide accurate cost projections. AI-powered estimating tools can assess material costs, labor requirements, and timelines, enabling more precise budgeting and resource planning. This leads to better financial management and reduces the likelihood of cost overruns.
Can AI replace builders?
While AI and automation are increasingly integrated into construction processes, they are not expected to replace human builders entirely. AI can handle repetitive tasks, data analysis, and machinery operation, but human expertise remains crucial for complex decision-making, craftsmanship, and managing unforeseen challenges on-site.
The future of construction will likely involve a collaborative approach, where AI augments human capabilities to improve efficiency and safety.
Stay Ahead With OpenAsset
The rise of AI-powered smart buildings is reshaping the way we design, construct, and manage modern infrastructure. From energy efficiency and predictive maintenance to advanced security and automation, AI is driving unprecedented innovation in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry. Therefore, firms that embrace tools with robust AI features will gain a significant competitive edge in optimizing workflow efficiencies.
A necessary tool that helps AEC professionals navigate this evolving landscape? DAM. OpenAsset, the leading Digital Asset Management (DAM) platform for AEC, helps AEC firms organize, access, and leverage visual assets to enhance project documents, marketing, and proposal development. OpenAsset ensures that firms stay ahead in an increasingly AI-driven industry.
Want to see how a DAM system with AI-powered features can transform your AEC workflow?





