As we step into 2024, the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry stands on the brink of a transformative era, driven by fast technological advancements, evolving environmental concerns, and shifting global economic landscapes.
The AEC sector, known for its resilience and adaptability, is positioned to embrace a wide range of innovative AEC industry trends that promise to reshape the future of construction, design, and infrastructure development. As industry professionals, stakeholders, and enthusiasts look to navigate these changes, understanding the impact and potential of these AEC industry trends is crucial.
In this blog, we delve into the top 17 AEC industry trends set to dominate the AEC industry in 2024, offering insights into how these developments are not just responding to current challenges but also paving the way for a more efficient, sustainable, and technologically integrated future.
Understanding the AEC Industry
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry focuses on the design, engineering, and construction of buildings, infrastructure, and other physical structures.
The industry covers a wide range of services dedicated to the planning and construction of both commercial and residential initiatives. It involves design and construction experts in the development and execution of projects that frequently reach multi-billion-dollar scales.
It’s a critical part of the economy, driving development and innovation in the built environment.
Moreover, the AEC industry plays a vital role in shaping our surroundings, impacting everything from the safety and functionality of the structures we use daily to the overall aesthetic and cultural significance of our communities.
Architecture
Architecture is the art and science of designing buildings and other physical structures. It is a discipline that blends creativity with technical knowledge to create environments that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Architecture is pivotal in determining the quality of our living and working spaces, influencing how we interact with our environment and each other.
Engineering
Engineering in the AEC industry includes a broad range of disciplines, including civil, structural, mechanical, electrical, and environmental engineering.
Engineers are responsible for the technical aspects of a project, ensuring that buildings and structures are safe, efficient, and sustainable. They apply principles of mathematics and science to solve problems and create solutions that meet the project’s specifications and regulatory requirements.
Construction
Construction is the process of turning architectural and engineering designs into physical reality. It involves the coordination of labor, materials, equipment, and technology to build or assemble infrastructure, buildings, and other structures.
Construction professionals, including contractors, project managers, and skilled tradespeople, work together to ensure projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
The Role of AEC in Driving Economic Growth
The AEC industry not only contributes directly to economic output through the creation of infrastructure and buildings but also acts as a catalyst for broader economic activities in several key ways.
Firstly, the AEC industry creates substantial employment opportunities. From architects and engineers to construction workers and project managers, the sector demands a diverse range of skills and labor, which helps to reduce unemployment and boost income levels within communities. The extensive supply chains associated with AEC projects—from raw materials to construction equipment—further multiply these employment effects across other industries.
Secondly, the infrastructure and buildings produced by the AEC industry are critical enablers of other sectors. Roads, bridges, ports, and railways are vital for efficient transportation and logistics, while commercial buildings, factories, and housing developments are essential for business operations, manufacturing, and residential living. These facilities lay the groundwork for economic activities, enhancing productivity and facilitating the smooth functioning of markets.
Moreover, investment in infrastructure is often seen as a stimulus for economic recovery and growth, especially during periods of economic downturn. Public spending on construction projects can drive economic activity by increasing demand, stimulating private sector investment, and improving business confidence. This fiscal multiplier effect is particularly pronounced in the construction sector due to its labor-intensive nature and the significant domestic material inputs required.
In addition to these direct and indirect economic impacts, the AEC industry also drives innovation and efficiency. Modern construction techniques and technologies (more on this later), such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), green building practices, and smart city designs, not only improve the sustainability and quality of built environments but also foster technological advancement and innovation across other sectors.
AEC Market Size and Growth
The global architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) market was valued at approximately USD 10.05 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.3% from 2024 to 2032, reaching about USD 24.36 billion by the end of the forecast period. This growth is primarily driven by advancements in BIM software, the increasing complexity of construction projects, and the expanding construction sectors across various regions.
Moreover, challenges such as economic fluctuations and the need for high initial investments can affect growth while the market’s expansion is further influenced by technological integration and the rising demand for eco-friendly building projects.
Regional Analysis of the AEC Industry
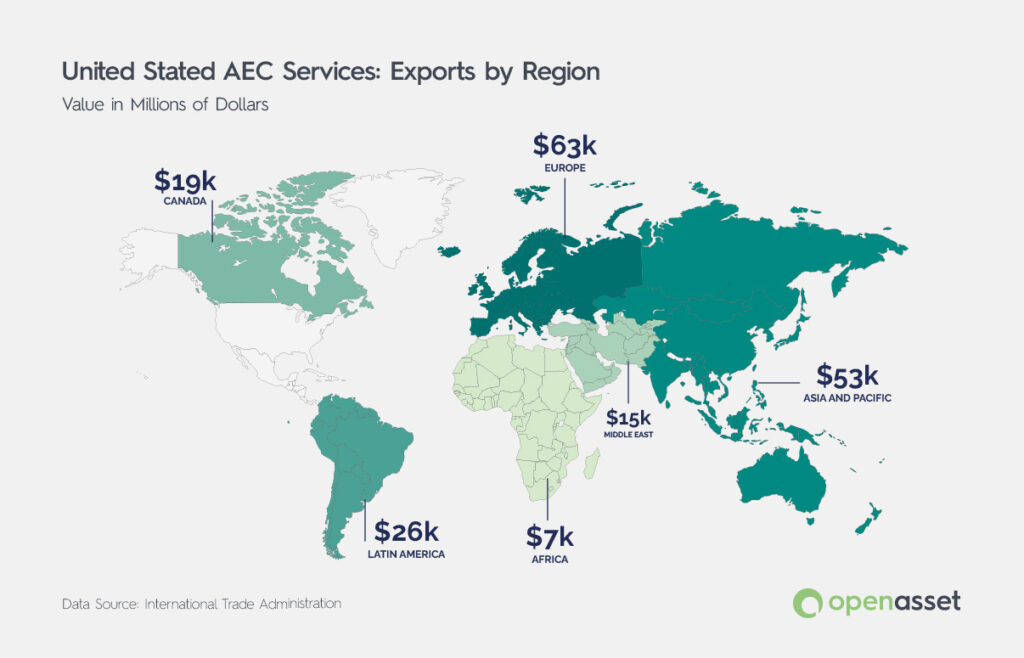
According to the International Trade Administration (ITA), from a regional perspective, between 2010 and 2021, Europe (33.96%) and the Asia Pacific (28.69%) regions held comparable shares of the U.S. AEC service export market. Initially, exports to the Asia Pacific were higher, but in 2013, Europe surpassed the Asia Pacific in receiving U.S. AEC service exports due to a decline in exports to the Asia Pacific rather than an increase to Europe. Since then, the gap has continued to widen, with Europe accounting for over 40% of U.S. AEC service exports in the last four years as demand from the Asia Pacific has declined. This decline in the Asia Pacific might be linked to China’s Belt and Road Initiative launched in 2013.
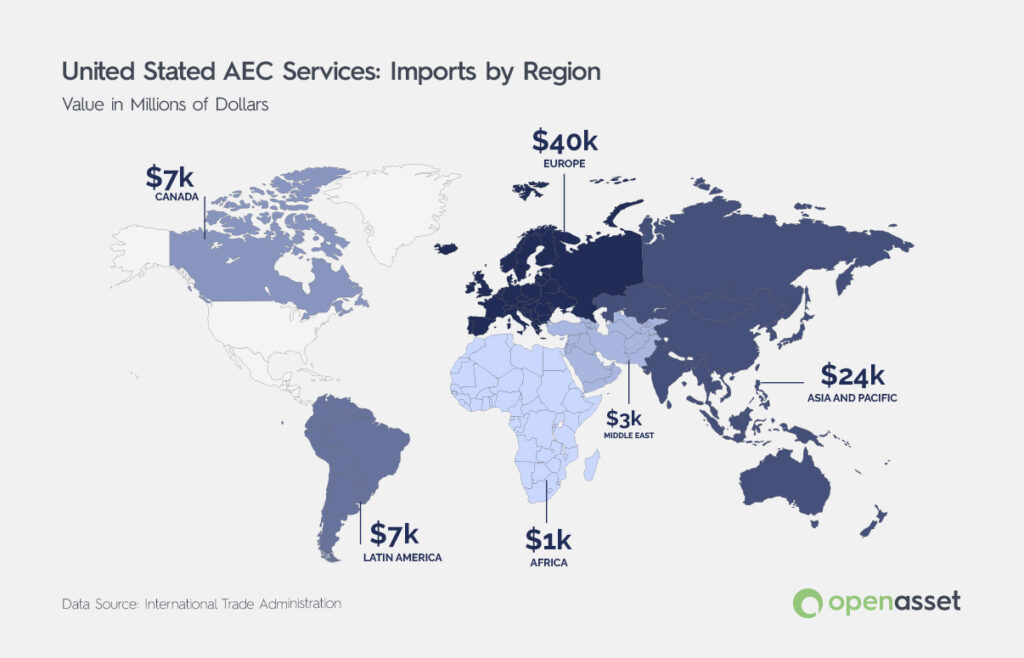
Conversely, the import dynamics tell a different story. From 2010 to 2021, Europe accounted for nearly half of the U.S. AEC service imports, while the Asia Pacific was responsible for 29.45% of imports. However, imports from the Asia Pacific have significantly increased over the last 11 years, rising from $577 million in 2010 to over $4 billion in 2021, whereas imports from Europe have remained relatively stable. Consequently, Europe’s share of U.S. AEC service imports dropped from 71.81% in 2010 to 34.98% in 2021, while the Asia Pacific’s share increased from 10.86% to 36.21% during the same period.
Top 17 AEC Industry Trends
Here are the top 17 AEC industry trends to keep an eye out for in 2024:
1. Digital Transformation
At the top of the AEC industry trends list is digital transformation. Digital transformation means the implementation of digital technology in all business areas. Within the AEC sector, it signifies the embrace of cutting-edge technologies and methodologies to refine the project lifecycle from start to finish.
In our AEC Outlook Survey, 74% of respondents said they plan to implement new technologies to help overcome key challenges. Additionally, McKinsey found seven key areas capable of boosting construction productivity by 50%-60%. One significant suggestion included integrating greater technology and innovation into the construction sector.
This shift is crucial for the AEC industry, allowing professionals to navigate past typical struggles and seize new opportunities. The adoption of digital tools equips AEC entities with the agility to navigate the dynamic market landscape effectively.
Key advantages of digital transformation in the AEC industry include:
- Crafting precise and comprehensive project models via Building Information Modeling (BIM).
- Enhancing project collaboration and information sharing through cloud solutions.
- Visualizing projects in immersive environments with Virtual Reality (VR).
- Extracting insights from extensive data sets using Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The journey towards digital transformation offers the AEC industry a wide range of improvements in proposal management, project execution, teamwork efficiency, and the design and construction process. The effects are profound, marking a significant leap towards innovation and efficiency across the project processes.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Second, in our AEC industry trends list is Artificial Intelligence (AI). In the AEC sector, the impact of AI on design and planning processes has been profound and transformative. AI algorithms now play a pivotal role in shaping and refining architectural concepts. They bring a new level of sophistication to space planning, ensuring optimal energy use, and elevating the aesthetic quality of projects.
By analyzing extensive datasets, AI provides insights that unlock new possibilities for creating designs that are not only visually appealing but also exceptionally functional and eco-friendly.
Moreover, AI and machine learning have introduced “generative design” methodologies, where algorithms generate new design options by synthesizing and recombining learned data in innovative ways. This capability of AI enhances the efficiency of the design process, ensures wiser use of materials, and leads to better project results overall.
Additionally, AI’s contribution extends significantly into structural planning, offering architects and engineers critical insights into the viability and structural integrity of their designs through advanced calculations and simulations.
This precision and foresight minimize the likelihood of mistakes and subsequent corrections, contributing to projects that meet their deadlines and budgets while upholding the utmost safety and quality standards.
AI-driven project management systems further revolutionize the industry by providing real-time updates, pinpointing potential delays, and analyzing a wide array of project variables.
3. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)
Next, in our AEC industry trends are Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). Virtual Reality (VR) offers a fully immersive experience, transporting users into a digitally created environment that takes over their visual field.
This total immersion allows architects and designers to deeply understand the spatial dynamics of a proposed design, simulating how individuals will interact with and navigate through the space. Such insights are crucial for refining the design to make the final structure as intuitive and user-centric as possible.
On the other hand, Augmented Reality (AR) blends digital elements with the real world by overlaying computer-generated imagery onto the user’s view of their physical surroundings. This enables AEC professionals to project full-scale 3D models into actual environments, simplifying the visualization of how a design integrates with its intended location.
Additionally, AR facilitates virtual tours of construction sites or proposed designs, offering clients a dynamic and engaging perspective far beyond static plans.
Utilizing AR and VR as simulation tools allows for a comprehensive analysis of a building’s potential performance under real-world conditions. Through this method, design and engineering groups can identify potential issues early in the project or utilize them throughout the construction phase to provide workers with a clearer picture of the final outcome.
Furthermore, AR and VR technologies enable stakeholders and potential users to explore new developments remotely, offering a virtual presence in spaces that are either under construction or in the planning stages.
This capability is immensely beneficial for AEC companies, helping in project management by aligning expectations, streamlining timelines, and helping to ensure projects are delivered within the projected budget and schedule.
4. Extended Reality (XR)
We’ve heard of AR and VR, but what is XR? And how can it help the AEC industry?
Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR), collectively referred to as XR or Extended Reality, transcend traditional interfaces for communication systems, introducing a transformative paradigm in the AEC industry. This includes everything from design and building processes to facility management, along with sales and marketing strategies.
By the year 2028, the global market for AR, VR, and MR is projected to grow to $250 billion, boasting a compound annual growth rate of 113.2%.
Currently, AEC professionals are harnessing XR technologies in cutting-edge workflows for design exploration and visualization, product development, enhancing construction rehearsals, advanced pre-visualizations, post-occupancy evaluations (POEs), immersive XR experiences, as well as training and facilitating remote collaboration for project teams worldwide.
Moreover, XR technologies enable AEC companies to distinguish their services with 3D renderings and visualizations, offering clients immersive virtual demonstrations of products. These presentations allow for the exploration of ideas and concepts in engaging ways that spark imagination and build trust.
Additionally, presenters can guide prospects through detailed virtual environments, elaborating on each aspect in real time for a comprehensive and interactive experience that surpasses what traditional BIM models could offer.
Furthermore, XR finds application in landscape architecture and urban planning, allowing for the creation of digital twins of proposed developments. Planners can simulate various scenarios within these digital twins to assess their effects on the environment, such as potential flooding or other environmental impacts.
XR also facilitates the creation of virtual tours for proposed projects, providing stakeholders with an in-depth understanding of the development and enabling the collection of valuable community feedback.
This innovative approach to project presentation and evaluation marks a significant advancement in how AEC projects are conceptualized, developed, and communicated.
5. Digital Twins
This year, digital twin technology is revolutionizing the construction landscape, offering unparalleled opportunities for the AEC sector. This makes it deserving of a space in our AEC industry trends list. Its potential to enhance various stages of a project, from planning and design through to construction, operations, and maintenance, is capturing the industry’s attention.
This technology offers comprehensive insights into the design and performance of a physical asset, capturing details about how spaces are used, occupant behaviors, traffic flows, and more.
These virtual replicas are dynamic, continuously evolving with real-time data to accurately reflect the current status of the physical asset. They enable immediate access to information across all aspects of a building.
Additionally, utilizing a Digital Twin allows for the exploration of “what-if” scenarios, and assessing the effects of design modifications, environmental changes, or security incidents within a unified digital environment.
This capability enables architects and project managers to foresee potential issues, refine building designs, and make more informed decisions quickly, leading to significant reductions in costs, delays, and improvements in project efficiency.
In fact, the strategic use of data from Digital Twins can reduce operating expenses by up to 35%, lower carbon footprints, and the creation of healthier work environments. However, these benefits only scratch the surface of what Digital Twins promise for the future.
In 2024, the integration of Digital Twins in construction projects is expected to become more widespread, fundamentally transforming the way we design, construct, and maintain buildings.
Far from being a fleeting trend, Digital Twins represent a significant stride forward, promising substantial benefits for AEC firms that are ready to embrace this innovative technology.
6. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
At the heart of digital solutions for AEC is Building Information Modeling (BIM). For those involved in construction projects, BIM software has likely become an indispensable part of the process.
This robust tool generates a 3D representation of a project, including crucial information such as dimensions, materials, and other relevant data. It transforms your building into a dynamic spatial database, incorporating scans, photographs, and various interactions, all tied to their real-world spatial coordinates.
This detailed digital blueprint of a building’s physical and functional attributes provided by BIM is essential for navigating the intricacies of design and construction. It promotes a unified and streamlined approach, empowering architects, engineers, and construction professionals to make well-informed choices.
The advantages are clear: construction becomes quicker and more cost-effective, and buildings are greener and simpler to manage.
7. Sustainability
While leveraging new technology is highly important, other factors, like sustainability are one of the AEC industry trends that is just as important.
Amidst a global push towards environmental preservation, the AEC sector is progressively adopting green practices to meet the increasing demand for sustainability.
Emerging sustainability AEC industry trends include:
- The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into architectural designs to decrease dependence on conventional energy supplies.
- The increasing use of green roofs and vertical gardens, which offer thermal insulation, enhance air quality and counteract the urban heat island phenomenon.
- The selection of recycled materials is on the rise, aiding in waste reduction and the conservation of natural resources.
- The pursuit of green building certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), sets the standard for sustainable construction by encouraging the development of buildings that are both energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
- Implementation of effective water management techniques, including rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling, to cut down on water use and support conservation efforts.
- The application of passive design principles, like strategic orientation, natural ventilation, and daylighting, is aimed at lowering energy usage while improving comfort for building occupants.
Additionally, AEC technologies are also crucial in creating designs that minimize carbon emissions, optimize water utilization, and efficiently use resources. By processing extensive data, these technologies can recommend eco-friendly materials and construction methods that comply with green building criteria.
Adopting innovative technologies and sustainable methodologies will be key to maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly changing AEC landscape.
8. Cloud Technology
Previously, challenges related to data storage and access represented significant obstacles within the AEC industry. However, the rise of cloud computing has markedly altered this landscape. By 2024, it is anticipated that cloud-based solutions will form the core infrastructure for the sector.
The appeal of cloud systems is rooted in their capacity to house extensive datasets, encompassing everything from architectural plans to construction timelines, and to provide access to this data anytime and from any location. This capability is particularly advantageous for project teams that operate across diverse geographical areas and time zones.
Furthermore, cloud platforms facilitate real-time updates and enable data-centric decision-making, ensuring cohesive collaboration across all team members.
Cloud computing also streamlines the sharing and collaborative efforts among project stakeholders, effectively bridging the gap created by physical distances. This advancement has fundamentally transformed teamwork dynamics, eradicating the conventional limitations posed by geographical separation.
The result is a significant enhancement in project efficiency, characterized by quicker completions, cost reductions, and a decrease in mistakes. For today’s AEC professionals, cloud systems have become indispensable, enabling them to remain interconnected and adaptable in the fast-paced global environment.
9. Drones
The integration of drone technology across AEC industries streamlines project workflows, from initial planning to completion, offering efficiency gains, enhanced safety, and a more sustainable approach to site management and material transportation.
In Architecture, using drones for land surveys equips architects with critical data for selecting the optimal site and direction for new buildings. The precise identification of existing structures, vegetation, utilities, and other potential obstructions is crucial during the initial design stages.
As the design progresses, integrating aerial photographs into drawings and visualizations offers a realistic preview of how the building will integrate with its actual surroundings.
In Engineering, drones play a pivotal role in tracking project advancement and creating accurate 3D models and 2D elevations of constructions as they are built. By comparing these real-time models with original engineering plans, engineers can verify the correct placement of structural components, thereby preventing costly errors.
Drone technology also facilitates thermal imaging to detect heat loss and other issues, enhancing the building’s efficiency. Moreover, it allows for safe and efficient structural inspections, eliminating the need for cranes, additional manpower, and the associated risks.
In the Construction sector, drones significantly refine the estimation and bidding process by providing detailed aerial views of the site, enabling contractors to assess the work required more accurately.
After construction begins, drone imagery aids in safeguarding materials and equipment against theft and enhancing site safety by identifying hazards. Beyond ground-level photography, drones offer an economical means of documenting the project’s progress for stakeholders and insurance verification.
In certain scenarios, drones may also contribute to transporting materials directly to the site, reducing environmental impact and streamlining logistics.
10. Leveraging Data
The AEC industry is quickly embracing a data-centric model. In 2024, the focus on data doesn’t just mean collecting information; it’s about leveraging information to make decisions that enhance efficiency and foster innovation.
In today’s construction landscape, data plays a pivotal role across all facets, from project identification to client management.
Therefore, having a platform that integrates data from a variety of sources, such as a CRM tool, offers a unified perspective that empowers teams. With such comprehensive insight, business developers and marketers can customize their approaches, find new opportunities, and have more robust relationships with clients.
The capacity to interpret and utilize this data dynamically revolutionizes the way AEC companies pursue projects and interact with clients. In an industry where accuracy and planning are key, adopting a data-driven strategy is not just advantageous but vital for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving sustained success.
11. AEC Workforce
The workforce within the AEC industry is undergoing significant transformation, influenced by several key trends and challenges. These changes are reshaping how AEC firms recruit, train, and manage their teams, with implications for the future of the industry.
Remote Work
72 % of respondents to Zweig Group’s AEC Workplace of the Future survey reported their firm changed remote/flexible work options after March 2020.
The shift towards remote work has been one of the most pronounced changes in the AEC workforce. Triggered by advancements in technology and further accelerated by global events, such as COVID-19, remote work has become a viable option for many within the industry.
This transition has allowed firms to tap into a broader talent pool, offering flexibility and reducing geographical constraints. However, it also necessitates robust digital infrastructure and effective communication tools to maintain collaboration and project management across distributed teams.
Skills Gap
According to a workforce survey, 89% are struggling to find enough qualified workers. The AEC industry is facing a growing skills gap, as the demand for new competencies, especially those related to emerging technologies like BIM, VR, and sustainable design, continues to rise.
This gap is exacerbated by an aging workforce and the challenge of attracting younger generations to careers in construction and engineering.
AEC firms are increasingly investing in training and development programs to upskill their workforce and are looking to educational institutions to produce graduates with the skills needed for modern construction projects.
Diversity
Diversity in the AEC workforce is another critical area of focus. Historically, the industry has struggled with diversity, particularly in terms of gender and ethnicity.
Increasing diversity not only enriches the workplace culture but also enhances creativity, innovation, and problem-solving capabilities within teams.
Efforts to promote inclusivity involve outreach programs to encourage underrepresented groups to pursue careers in architecture, engineering, and construction, as well as policies and practices that support a more diverse and inclusive workforce.
The AEC workforce is at a crossroads, with remote work, the skills gap, and diversity shaping its future direction. Addressing these challenges is essential for firms looking to remain competitive and innovative in an evolving industry landscape.
12. Adaptive Design
The movement towards adaptive design stands as a pivotal shift towards sustainability in our future. With the increasing awareness of climate change’s implications on our built surroundings, there’s a growing focus on developing designs that are both resilient and adaptable.
This requires that engineers integrate strategies to counteract the repercussions of extreme weather, rising sea levels, and other phenomena associated with the climate crisis in their projects.
Challenges such as the aging of existing structures and the scarcity of land for new urban development are prevalent issues across the globe. The degradation of urban assets, including buildings, infrastructure, and public spaces, is prompting cities and governing bodies to explore the renovation, restoration, and repurposing of these elements.
More recently, the preference among clients to upgrade their current assets into more modern, efficient, and technology-rich facilities is noticeable. This shift not only enhances the functionality but also contributes to significant carbon savings by favoring preservation over demolition and new construction.
13. Efficient Water Management
The concept of a water footprint includes the entire volume of freshwater utilized, both directly and indirectly, by individuals, communities, or organizations. This includes water consumption involved in the production and use of goods and services.
In the AEC industry, operations significantly impact water resources. The demand for water in construction processes like concrete mixing, site preparation, and landscaping is immense.
Recent instances of sewage discharges by major water companies have heightened awareness regarding the impact on water quality.
As a result, there is an increasing requirement for projects to demonstrate their non-adverse effects on watercourses. Strategies for efficient water use, including rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling, are being adopted more widely to reduce consumption and support conservation efforts.
The industry is also exploring innovative uses of natural water bodies as thermal energy sources for heating and cooling systems, reminiscent of the earlier surge in hydropower applications.
This initiative is part of broader efforts by energy specialists to discover sustainable heating and cooling solutions for new projects, aiming to lower the carbon emissions associated with these systems.
At the foundation of effective water resource management lies the resurgence of an integrated approach to the water cycle. Advances in computing, such as AI and machine learning, offer the potential to move beyond compartmentalized management strategies, fostering a more cohesive and sustainable framework for water conservation.
14. Implement Integrated Solutions
For many leaders in the AEC industry, a key goal is to achieve comprehensive connectivity across their organization. The modern connected AEC firm utilizes holistic business systems, cloud technology, and sophisticated analytics to gain a complete overview of the company.
This approach not only streamlines operations and fosters collaboration but also empowers firms to effectively manage their business.
Because the AEC sector is characterized by complex workflows, it demands the seamless setup of various components. Integrated solutions serve as the critical link that ensures cohesion among these components.
As we move through 2024, the emphasis is on achieving seamless integration—where project management extends beyond conventional limits to embrace every phase of construction, from initial planning through to final execution.
A Digital Asset Management (DAM) tool specifically designed for the AEC industry, like OpenAsset, streamlines workflows by integrating with various software systems like ERP and project management tools crucial in the AEC industry.
Moreover, this integration consolidates data, enhancing its accessibility and simplification for better-informed decision-making. This unified approach streamlines processes, reduces miscommunication, and promotes an open, cooperative atmosphere.
In a sector where efficiency equates to financial savings and time is of the essence, solutions that enable smooth integration across diverse platforms and systems are indispensable. They are transforming the operational dynamics of the AEC industry, establishing integrated solutions as a necessity rather than just an option.
15. Laser Scanning
Last, but not least, on our list of AEC industry trends is laser scanning. Laser scanning devices offer a groundbreaking method for collecting and visualizing data, delivering exceptionally detailed and accurate representations of physical spaces.
Integrating 3D laser scanners represents a significant technological jump that has attracted widespread interest. This innovation has transformed the AEC industry by enhancing accuracy, saving time, and improving cost-effectiveness.
3D laser scanners, capable of capturing millions of data points in seconds, generate precise as-built models, cutting measurement inaccuracies by up to 70%. Such accuracy improves the overall quality of design and construction workflows.
Moreover, 3D laser scanning eliminates the need for manual measurements, accelerating the data collection process, speeding up project timelines, facilitating quicker decision-making, and minimizing project holdups.
The adoption of 3D laser scanning technology could markedly change the practices of AEC professionals, ushering in a new era of precision and efficiency.
16. Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Modular and prefabricated (or prefab) construction methods involve producing building components or entire structures in a controlled, off-site environment, such as a factory. Once these components are fabricated, they are transported to the construction site and quickly assembled, drastically cutting down the time and labor typically required by traditional construction methods.
The growing adoption of these methods is driven by several compelling advantages. Firstly, construction time is significantly reduced as components are manufactured off-site in a controlled setting. This leads to faster on-site assembly, often cutting the construction timeline by as much as 50% when compared to traditional methods.
This method also enhances quality control, as the factory environment allows for stricter oversight, reducing errors and ensuring a consistently high standard of construction. Cost-effectiveness is improved as well, since prefab reduces labor expenses, cuts down on material waste, and streamlines overall project management, resulting in considerable cost savings.
Additionally, modular and prefab constructions support sustainability efforts by minimizing construction waste and environmental disruption while facilitating the easy incorporation of energy-efficient technologies. Despite the standardization, these methods still offer design flexibility, allowing for customization to meet diverse project requirements.
17. 3D Printing
3D printing is rapidly becoming a pivotal trend in the AEC industry, revolutionizing the way buildings and infrastructure are designed and built. Known as additive manufacturing, this technology enables the creation of complex and customized structures that traditional construction methods struggle to achieve.
Architects and engineers now have the freedom to explore intricate designs and innovative forms, pushing the boundaries of architectural aesthetics and functionality. This increased design flexibility is complemented by enhanced construction efficiency, as 3D printing allows for the fast production of building components directly from digital models, reducing project timelines and labor costs through minimal manual intervention.
Beyond design and efficiency, 3D printing offers significant cost benefits and sustainability advantages. The technology minimizes waste by using only the necessary amount of material, often incorporating recycled materials, which helps reduce the environmental impact of construction projects.
Moreover, producing materials on-site or nearby cuts down on transportation costs and emissions, aligning with the industry’s growing commitment to sustainable practices.
Lastly, as 3D printing technology integrates with other digital tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM), it paves the way for more automated and efficient construction processes. This trend not only enhances the capability and efficiency of the AEC industry but also fosters a shift towards more environmentally responsible and economically feasible construction practices.
AEC Industry Challenges
The AEC industry faces several significant challenges that impact its efficiency, productivity, and overall success. These challenges are multifaceted, ranging from workforce issues to regulatory hurdles. Here’s a closer look at some of the key challenges:
Labor Shortages
The U.S. AEC services industries are consistently facing labor shortages, with the demand for AEC services surpassing the supply that the industries can provide.
Labor shortages have been affected by several factors, including an aging workforce, the cyclical nature of construction work, and the industry’s difficulty in attracting younger generations who often seek careers in less physically demanding and more technologically focused fields.
The shortage of skilled labor affects all levels of the industry, from on-the-ground workers to specialized professionals like engineers and project managers. This lack of available and qualified workers can lead to delays in project timelines, increases in labor costs, and even compromises in the quality of work.
Additionally, as the demand for construction continues to grow, particularly in developing regions and in sectors such as infrastructure and green building, the gap between the supply of skilled workers and the industry’s needs widens even further.
Efforts to address these labor shortages have included increasing investment in training and apprenticeship programs, improving working conditions and wages to attract more candidates, and leveraging technology to streamline construction processes and reduce the physical burden on workers.
Moreover, there is a growing focus on diversity and inclusion initiatives aimed at widening the pool of potential employees by encouraging more women and underrepresented groups to consider careers in the AEC field.
Skills Gap
Another challenge we mentioned earlier is the skills gap. As the sector continues to evolve with technological advancements and shifting market demands, there is a growing need for professionals who are not only skilled in traditional construction practices but are also proficient in modern technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), sustainable design practices, etc.
This gap between the skills possessed by the existing workforce and those required to efficiently execute modern, technologically advanced projects is causing concerns about the industry’s ability to adapt and thrive. Many current workers need additional training to keep pace with new industry standards, while educational institutions often struggle to update curricula quickly enough to meet the demands of the evolving field.
The disparity is further intensified by a generational turnover, with a significant portion of the skilled workforce nearing retirement, and not enough young talent entering the field to replace them. The AEC industry must address this gap through targeted efforts such as enhancing education and training programs, fostering partnerships with academic institutions, and investing in continuous professional development and certification programs.
Additionally, firms can bridge this gap by promoting more inclusive hiring practices to attract a diverse range of candidates and by providing robust on-the-job training to equip their workforce with the necessary skills. Addressing the skills gap is essential for the AEC industry to remain competitive and capable of meeting the complex challenges of modern construction and design.
Safety Concerns
Given the inherent risks associated with building and construction work, including the use of heavy machinery, work at heights, and the handling of hazardous materials, ensuring the well-being of workers is a critical priority. Despite advancements in safety equipment, training, and regulations, the AEC sector still experiences a relatively high rate of workplace accidents and injuries compared to other industries.
The complexity of construction projects often contributes to these safety challenges, as sites are dynamic environments with constantly changing hazards. Ensuring that safety measures keep pace with these changes requires diligent management and ongoing vigilance. Moreover, there is a need for continuous education and training for all employees to foster a safety-first culture within organizations.
Additionally, the adoption of new technologies and techniques can sometimes introduce new risks, especially if there is insufficient training or understanding of these innovations. Therefore, while technology holds the promise of making construction sites safer, it also necessitates careful implementation and oversight.
Addressing these safety concerns effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes strict adherence to safety protocols, regular safety training for all levels of personnel, investment in the latest safety technologies, and a corporate culture that prioritizes safety above all.
High Costs
70% of organizations either have a digital transformation strategy or are currently working on one. However, the integration of advanced digital technologies—such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI)—requires substantial financial investment.
This includes costs for acquiring software licenses, upgrading hardware, and securing data storage and management solutions. Additionally, there is often a need for ongoing maintenance and updates to keep these digital tools functioning optimally.
Beyond the direct costs of technology acquisition, there are substantial expenses associated with training and development. AEC firms must invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure that their workforce can effectively utilize new technologies. This is crucial for maximizing the potential benefits of digital tools, such as improved efficiency and accuracy in project planning and execution.
Moreover, the shift to digital operations can lead to indirect costs, such as the time lost during the transition period and potential temporary reductions in productivity as teams adapt to new systems. The challenge of justifying these upfront and ongoing investments can be particularly daunting for smaller firms with limited budgets.
Therefore, while digital transformation promises long-term gains in efficiency, cost control, and competitive advantage, the initial and sustained financial outlays pose a considerable barrier to its adoption within the AEC industry.
Regulations and Compliance
The AEC industry is heavily regulated, with firms needing to comply with a wide range of local, national, and international regulations. These can include building codes, environmental protections, labor laws, and safety standards.
Navigating this complex regulatory landscape can be challenging, particularly as regulations may change or vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders in the AEC industry.
Strategies may include investing in workforce development and training programs, embracing technological innovations to improve productivity and safety, and advocating for regulatory reforms that support industry growth while ensuring high standards of quality and safety.
Change Management
As the AEC sector experiences rapid technological advancements and shifts in regulatory landscapes, organizations must adeptly manage these changes to stay competitive and efficient. Change management in the AEC industry involves adapting to new processes, technologies, and standards that can dramatically alter traditional workflows and project execution strategies.
Effective change management is critical for integrating innovative technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), prefabrication, and green building practices into everyday operations. These changes not only require significant investment in new software and equipment but also demand comprehensive staff training to ensure proficiency and efficiency in using new tools.
However, the challenge doesn’t end with implementation. The dynamic nature of the AEC industry means that firms must be continuously prepared to evolve and adapt. This requires a cultural shift towards flexibility and learning within organizations, where change is not only managed but embraced as a constant element of the industry’s landscape.
Therefore, successful change management in the AEC sector involves a blend of strategic planning, continuous education, and an organizational culture that promotes adaptability and resilience.
Emerging Future Trends in the AEC Industry
As the AEC industry moves forward, it faces a landscape deeply influenced by rapid technological advancements and evolving regulatory frameworks. Here’s a look at some of the key trends that will shape the future of AEC:
Technology’s Impact on AEC Firms
The adoption of cutting-edge technologies is reshaping AEC firms from the ground up, enhancing everything from project planning to execution. Technologies such as AI, BIM, and cloud computing are streamlining workflows and improving efficiencies across projects.
Robots on Construction Sites
The global construction robots market size was valued at USD 1,028.6 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.5% from 2023 to 2030. Robotics technology is increasingly becoming a fixture on construction sites, offering precision and efficiency that surpass traditional methods. From automated bricklaying to drones for surveying, robots are setting new standards for speed and accuracy in construction.
Enhancing Standards and Regulations
As the industry evolves, so too does the regulatory landscape. New standards are continually being developed to ensure safety, sustainability, and quality in construction, pushing firms to adapt to these changes proactively.
Data Security in the AEC Sector
With the increasing digitization of architectural and construction processes, protecting sensitive project data has become paramount. Firms must invest in robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against data breaches and cyber threats.
Advancements in Education and Training
The growing skills gap in the AEC industry is prompting a renewed focus on education and training. Modern curricula are beginning to reflect the need for tech-savvy professionals who are proficient in the latest construction technologies and methodologies.
Tips for AEC Industry Professionals
For professionals in the AEC industry, staying ahead involves continuous learning and adaptation. Here is actionable advice to help you thrive in this dynamic field:
- Embrace technological advancements; familiarize yourself with tools like BIM software, drones, and AI applications that can enhance accuracy and efficiency on projects.
- Prioritize developing soft skills such as project management and effective communication, as these are crucial for leading teams and managing client expectations.
- Commit to lifelong learning by attending workshops and certifications in emerging areas like sustainable design and smart construction.
- Actively participate in industry networks and forums to exchange ideas and stay updated on regulatory changes and market trends.
By integrating these practices, AEC professionals can better navigate the complexities of the industry and propel their careers forward.
Resources for AEC Business Growth
Curious to learn more about growing your AEC firm while adapting to future technology trends? Here are some helpful resources from OpenAsset:
- Understanding AI in DAM and How It’s Transforming Asset Management
- AI In Architecture
- Building the Future: How AI is Transforming the AEC Industry
- 2022 AEC Industry Outlook Survey
Shaping the Future of the AEC Industry With OpenAsset
As an AEC professional, achieving and maintaining a competitive edge requires not only expertise and innovation but also the adoption of efficient tools for managing and leveraging digital assets.
OpenAsset is crucial for AEC firms aiming to streamline their workflows, enhance collaboration, and manage digital content effectively.
It centralizes digital assets in one accessible location, significantly reducing the time spent searching for files across different systems. This centralization fosters enhanced collaboration by ensuring easy access to project assets for team members, regardless of their geographic location.
Furthermore, OpenAsset’s seamless integration with industry-standard tools simplifies incorporating asset management into existing project workflows, facilitating smooth project progression with all necessary assets readily available.
With OpenAsset it’s simple: Centralize AEC assets. Create more proposals. Win more business. Ready to try it out for yourself?



